ELK Setup Automation
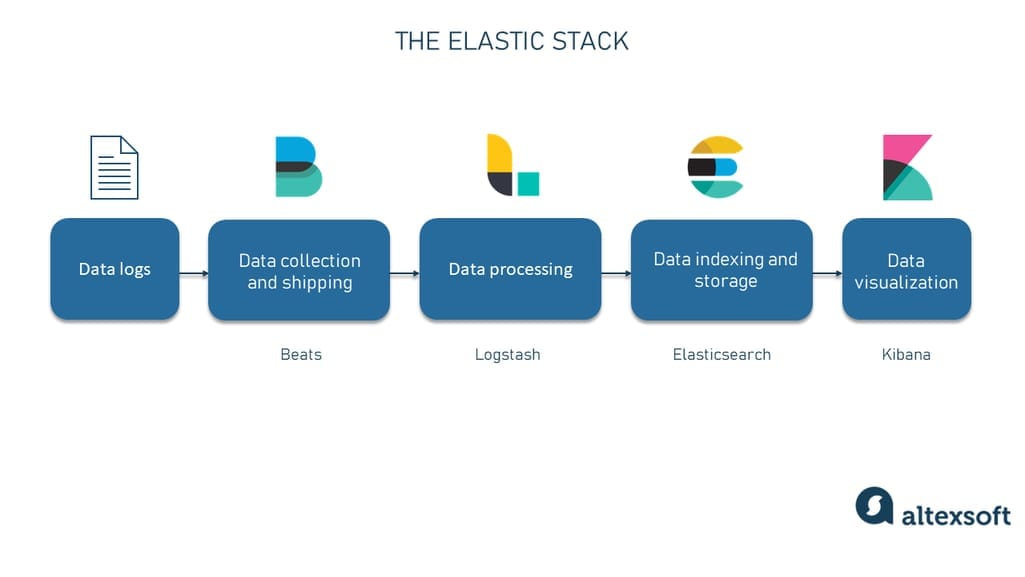
Project Overview
Setting up an Elasticsearch cluster across multiple nodes is often repetitive, error-prone, and difficult to reproduce. This project provides an automated and repeatable setup for deploying a multi-node Elasticsearch cluster with Kibana, reducing manual configuration and operational risk.
The solution focuses on automation, consistency, and operational verification, ensuring the cluster is correctly configured and observable after deployment.
Problem Statement
Manual ELK stack installation introduces several challenges:
- Repetitive and time-consuming node configuration
- High risk of misconfiguration across multiple nodes
- Difficult cluster validation after setup
- Limited visibility into setup failures
These issues slow down infrastructure provisioning and reduce reliability in production environments.
Solution Overview
This project delivers an automated ELK setup workflow using encoded setup scripts and trigger mechanisms:
- Automated Elasticsearch cluster setup across multiple nodes
- Obfuscated setup scripts to protect configuration logic
- Trigger scripts to execute node-specific configurations
- Built-in verification steps to validate cluster health and node status
- Kibana integration for observability and monitoring
The setup emphasizes repeatability, operational safety, and post-deployment verification.
Architecture & Workflow
The workflow follows a clear operational sequence:
- Encoded setup scripts configure Elasticsearch nodes consistently.
- Trigger scripts execute the setup on each target node.
- Elasticsearch services are started and joined into a cluster.
- Cluster health and node membership are verified via REST APIs.
- Kibana is validated to ensure correct connectivity to Elasticsearch.
- Logs are generated at each step to assist with troubleshooting.
This approach ensures that infrastructure is not only deployed, but also validated and observable.
Cluster Verification
After deployment, the cluster is validated through multiple checks:
- Cluster health is queried to ensure proper node coordination.
- Node information is retrieved to confirm all nodes are active and correctly registered.
- Service recovery is supported by restarting Elasticsearch services when nodes are unavailable.
These steps ensure the cluster is operational and resilient after setup.
Kibana Verification
Kibana is included to provide visibility into the Elasticsearch cluster:
- Service status checks confirm Kibana is running correctly.
- Web access verifies the UI is reachable on the default port.
- Connection validation ensures Kibana is properly linked to Elasticsearch using built-in tools.
This guarantees that monitoring and observability are available immediately after deployment.
Logging & Observability
Each setup step produces logs that capture:
- Successful executions
- Configuration failures
- Service startup issues
These logs support fast debugging and make the automation suitable for real infrastructure environments.
Outcomes & Impact
The project delivers tangible operational value:
- Faster ELK cluster provisioning
- Reduced configuration errors across nodes
- Repeatable and consistent deployments
- Immediate observability through Kibana
- Easier troubleshooting through structured logs
The automation transforms ELK setup from a manual process into a reliable infrastructure workflow.
Key Learnings
- Infrastructure automation significantly reduces operational risk.
- Verification and observability are critical parts of deployment, not afterthoughts.
- Encapsulation of setup logic improves maintainability and security.
- Production-ready systems require validation, not just installation.
Conclusion
An automated solution for deploying and validating a multi-node Elasticsearch cluster with Kibana, reducing setup time, configuration errors, and operational complexity.