JupyterHub on Kubernetes
Overview
JupyterHub on Kubernetes with Task Queue and Resource Optimization is a high-availability platform designed to support multiple users running Jupyter notebooks in parallel for AI, ML, and scientific computing workloads. The system integrates dynamic resource scheduling, persistent storage, and container orchestration, ensuring fair distribution of CPU/GPU resources and uninterrupted access to user environments.
This project was completed as a Final Year Project for the National Engineering Degree in Computer Science, Data Engineering Option – Faculty of Sciences of Sfax, showcasing expertise in scalable, production-ready data platforms.

Deployment Architecture
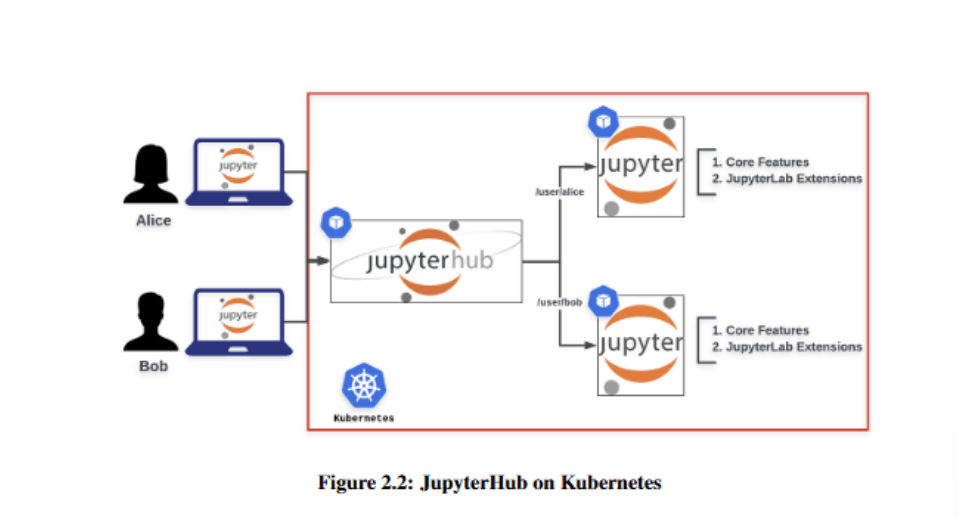
- High-Availability Kubernetes Cluster: Three master nodes with HAProxy for load balancing and worker nodes hosting JupyterHub environments.
- Persistent Storage: NFS provides shared storage across all pods, ensuring users’ notebooks and data are preserved.
- Dynamic User Environments: Each user is provisioned a dedicated JupyterLab instance, dynamically managed by Kubernetes for scalability and isolation.
- Resource Optimization: Apache YuniKorn manages CPU/GPU scheduling with a task queue, ensuring fair and efficient allocation across multiple users.
Technologies Used
- Kubernetes: Container orchestration, high availability, and fault tolerance
- JupyterHub: Multi-user management of isolated JupyterLab environments
- Helm: Deployment automation and package management
- Apache YuniKorn: Fine-grained task scheduling for CPU/GPU workloads
- NFS: Shared persistent storage for notebooks and user data
- HAProxy: Load balancing for Kubernetes master nodes
Key Features
- Multi-user access to isolated, production-ready Jupyter environments
- Dynamic, fair CPU/GPU resource scheduling with YuniKorn
- Persistent notebook storage for reliable user data management
- High-availability cluster architecture to minimize downtime
- Support for resource-intensive AI/ML and scientific computing workloads
Business & Technical Impact
This platform demonstrates the ability to deploy and manage complex, scalable, and high-performance data infrastructures. It highlights skills in cloud-native architecture, container orchestration, resource optimization, and multi-user platform management, enabling organizations to maximize hardware utilization, ensure data persistence, and support intensive computational workloads.
Future Improvements
- Monitoring & Observability: Integration with Prometheus and Grafana for real-time visualization of CPU/GPU/memory usage and custom dashboards for cluster administration.